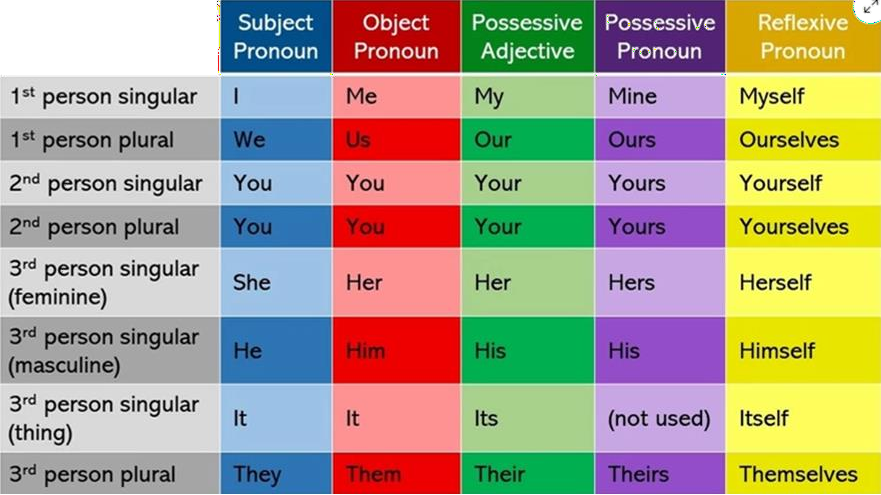
Rule 1 Subject Pronoun
Subject pronouns are used when the pronoun is the subject of the sentence. You can remember subject pronouns easily by filling in the blank subject space for a simple sentence.
Example:……..did the job.
I, he, she, we, they, who, whoever, etc., all qualify and are, therefore, subject
pronouns.
Rule 2 Object Pronouns me, him, her, us, them, themselves, herself.
Example: Jean saw him.
➸ “Him” is the direct object of the verb saw.
Rule 3
The pronouns who, that, and which become singular or plural depending on the
subject. If the subject is singular, use a singular verb. If it is plural, use a plural verb.
Example 1: He is the only one of those men who is always on time.
➸ The word ”who” refers to ”only one”. Therefore, use the singular verb ”is”.
Sometimes we must look more closely to find a verb’s true subject.
Example 2: He is one of those men who are always on time.
➸ The word ”who” refers to ”men”. Therefore, use the plural verb are.
Rule 4
Pronouns that are singular (I, he, she, everyone, everybody, anyone, anybody, no one, nobody, someone, somebody, each, either, neither, etc.) require singular verbs. Each of the girls sings well.
Either of us is capable of doing the job.
Neither of them is available to speak right now.
Rule 5
The possessive pronouns yours, his, hers, its, ours, theirs, and whose never
need apostrophes. Avoid mistakes like her’s and your’s.
Examples: It’s been a cold morning.
The thermometer reached its highest reading.
Rule 6
Pronouns that end in -self or -selves are called reflexive pronouns. There are nine reflexive pronouns: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, oneself, ourselves, yourselves, and themselves.
Reflexive pronouns are used when both the subject and the object of a verb are the
same person or thing.
Example: Joe helped himself.